GNSS converter
If you own an Argonaut or Medea receiver you are probably wondering how to
convert the .rok files into something else, or how to extract both the
IMU data as well as the time events (if present in the file). Jason provides,
free of charge, a converter that does that.
First of all login to the service and head towards the GNSS converter (at the top of the page). You should see the following page:
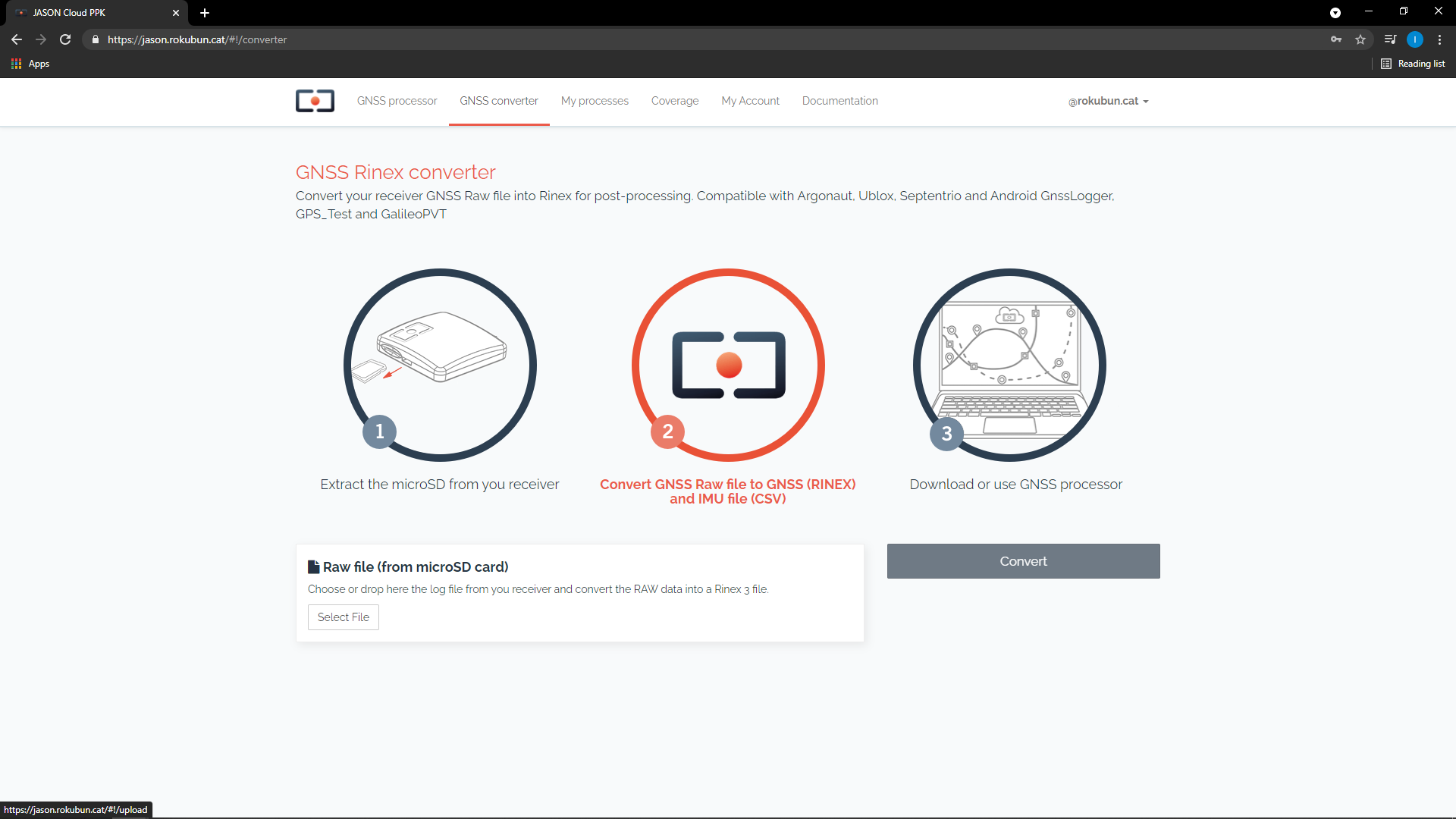
Simply drag and drop the file you want to process in the Raw file
box and press convert. Once the process is finished, press Download zip to
fetch the data. Assuming that the you uploaded a file named <input_file>, you
should see the following files:
<input_file>.rnx: The Rinex file (version 3.03) with the GNSS raw measurements recorded by the receiver<input_file>.rnx_imu.csv: A columnar file with the IMU data, time tagged in GPS time. See the complete format description here.<input_file>.rnx_cam.csv: A columnar file with the event data (e.g. camera event data). See the complete format description here.
Actually, if you have a receiver that ships a ublox receiver, not necessarily our own, you can still use the tool to convert to Rinex file. However we will always deny you can do it ;P
Converted files
This section includes a description of the files delivered by the GNSS converter
Argonaut GNSS file
Rokubun's Argonaut/Medea receivers store GNSS in Ublox format. The output of the GNSS converter in terms of GNSS measurements data will be the equivalent RINEX 3.03 file as follows:
3.03 OBSERVATION DATA M (MIXED) RINEX VERSION / TYPE
Rokubun core rokubun 2019-08-12 15:43:35 PGM / RUN BY / DATE
UNKN MARKER NAME
unknown unknown OBSERVER / AGENCY
unknown unknown unknown REC # / TYPE / VERS
unknown unknown ANT # / TYPE
0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 APPROX POSITION XYZ
0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 ANTENNA: DELTA H/E/N
2019 06 05 01 52 03.7652649 TIME OF FIRST OBS
G 4 C1C L1C D1C S1C SYS / # / OBS TYPES
R 4 C1C L1C D1C S1C SYS / # / OBS TYPES
E 4 C1C L1C D1C S1C SYS / # / OBS TYPES
END OF HEADER
> 2019 06 05 01 52 20.2019999 0 6
G05 21643026.31606 113734869.95806 -2084.85906 40.00006
G13 20940404.71107 110042563.43007 650.48707 45.00007
G15 21819537.83307 114662444.00207 2552.08207 46.00007
G29 22272808.61807 117044397.73607 -2139.16707 45.00007
G30 24262711.51305 127501402.06305 -245.06005 34.00005
E13 24476988.50208 128627441.38908 970.55808 49.00008
Argonaut IMU file
Rokubun's Argonaut/Medea receivers store GNSS data as well as IMU data from its
inertial sensor. This data is syncrhonized with the GPS time scale and stored
in the SD card along with the GNSS raw measurements. When using the conversion
tool from Jason, a CSV file with the IMU data will be generated. The file starts
with a comment line (starting with #) that describes each column as well as
the appropriate units:
gps_weekThe GPS week of the time stampgps_towThe seconds of the GPS weekmag_x,mag_y,mag_z, 3 components (XYZ) of the magnetometer, expressed in micro-Teslasgyro_x,gyro_y,gyro_z, 3 components (XYZ) of the gyroscope, expressed in degrees per secondaccel_x,accel_y,accel_z, 3 components (XYZ) of the accelerometer, expressed in g's (9.81 m/s^2)
All inertial values are referred to the body reference frame. Check the Argonaut/Medea documentation for further details.
Example of IMU file:
# Imu,gps_week,gps_tow[seconds],mag_x[uT],mag_y[uT],mag_z[uT],gyro_x[deg/s],giro_y[deg/s],giro_z[deg/s],accel_x[g],accel_y[g],accel_z[g]
Imu,1990,210938.388921000,-8.400,56.550,-33.600,-2.305,-0.580,0.641,-0.007,0.053,-0.983
Imu,1990,210938.398899000,-9.000,55.800,-31.200,-2.290,-0.641,0.626,-0.015,0.060,-0.980
Imu,1990,210938.408876000,-7.650,53.700,-33.150,-2.275,-0.702,0.626,-0.010,0.053,-0.985
Imu,1990,210938.518632000,-9.750,56.250,-32.250,-2.275,-0.565,0.626,-0.008,0.054,-0.981
Imu,1990,210938.528610000,-9.000,55.800,-33.900,-2.290,-0.504,0.626,-0.007,0.059,-0.979
Imu,1990,210938.538588000,-10.500,55.200,-34.200,-2.275,-0.458,0.641,-0.008,0.057,-0.987
Imu,1990,210938.548566000,-9.000,56.250,-33.600,-2.275,-0.458,0.641,-0.015,0.057,-0.980
Imu,1990,210938.558543000,-7.650,56.250,-33.600,-2.275,-0.473,0.626,-0.013,0.058,-0.988
Imu,1990,210938.593055000,-9.300,55.950,-33.000,-2.305,-0.489,0.641,-0.015,0.059,-0.979
Imu,1990,210938.603033000,-8.550,54.900,-33.450,-2.290,-0.489,0.626,-0.016,0.056,-0.978
Imu,1990,210938.613011000,-9.000,56.850,-33.150,-2.305,-0.550,0.626,-0.012,0.056,-0.982
Imu,1990,210938.622988000,-10.200,55.200,-32.850,-2.305,-0.580,0.626,-0.012,0.059,-0.984
Argonaut CAM file
In addition, Argonaut/Medea receivers store any time event that has been triggered during the data recording campaign by means of a hot-shoe mounted on a photogrammetry SLR camera or MicaSense. Converting a file that contains time (cam) events will result in the generation of a file with 2 columns: (1) the GPS week and (2) the seconds within the GPS week when the time event took place.
The file has as many rows as events detected by the receiver and the time tag is synchronized to the time scale provided by the GNSS receiver.
If no cam events have been detected, no file will be generated.
Example of CAM (time event) file:
# Event,gps_week,gps_tow[seconds]
Event,1990,211188.789716000
Event,1990,211193.854405000
Event,1990,211198.683787000
Event,1990,211201.679891000
Event,1990,211374.665552000
Event,1990,211377.808189000
Event,1990,211380.612900000
Event,1990,211383.346676000
Event,1990,211385.930332000
Third party options
If you'd rather convert the files yourself without using our platform, you just
have to know that any tool that is able to parse ublox binary format (ubx) will
convert your files into Rinex format. Two examples are UNAVCO's teqc and RTKLIB's
convbin (or its Windows GUI equivalent rtkconv).
The resource section of this documentation contains links on how to obtain them. Note however, that you will have to download these tools yourself or, if you are familiar with Docker, we compiled an image (rokubun/gnss_tools) with these tools included (and much more).
For the examples given in the following sections, you will need the sample rok file argonaut_cam.rok.
teqc
To convert the rok file into Rinex 2 (adding some header fields), use the
following command:
marker_name="ARGO"
rx_type="argonaut"
ant_type="internal/patch"
teqc -ublox ubx -O.rt ${rx_type} -O.at ${ant_type} -O.mo ${marker_name} argonaut_cam.rok > argo0580.18o
convbin
If you'r rather use convbin, please use this command (to output the data in
Rinex 3.03 format):
marker_name="ARGO"
rx_number="03018-1-0xxx"
rx_type="argonaut"
ant_type="internal/patch"
convbin -v 3.03 -od -os -r ubx -o argo0580.18o -hr "${rx_number}/${rx_type}/" -ha "/${ant_type}" -hm ${marker_name} argonaut_cam.rok